ICSE 10 Physics Competency Based Questions Solution
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 36. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
Anu and Amy purchased ice creams in plastic balls and cones, respectively, during their outing at the science fair. After consuming their ice creams, Anu stated that regardless of whether they were filled with ice cream or empty, the centre of gravity of the objects would remain unchanged. Do you agree with Anu? Why?
Answer: No, I do not agree with Anu.
The Centre of gravity of the sphere remains the same, while the C.G. of hollow cones and solid cones are different. C.G. of hollow cone from base is h/3 and of solid cone is h/4 from base.
Question 37. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
The picture below shows a boy climbing a rope ladder hanging from the branch of a tree. The boy in the picture finds it difficult to climb the ladder as it turns about the axis where he is holding. The instructor tells the boy to stretch the body with the hands stretched up and make the body parallel to the ladder and climb.

(a) Which force caused the ladder to turn?
(b) How does keeping the body parallel to the ladder make climbing easier?
Answer: (a) His own weight causes the torque on his body and turns about his hands holding the ladder.
(b) By stretching and keeping the body parallel to the rope, the torque arm is decreased, which reduces the torque and makes it easier to climb.
Question 38. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
Regenerative braking involves harnessing the energy that is typically lost when a car decelerates and brakes and instead using it to recharge the car’s batteries. Unlike traditional braking systems that simply dissipate energy, regenerative braking allows some of that energy to be recycled.
(a) What is the energy conversion process that results in the wastage of energy in a normal car during braking?
(b) How does regenerative braking differ from normal braking in terms of energy conversion?
Answer: (a) Kinetic energy to heat energy (due to friction).
(b) Regenerative braking converts kinetic energy to electrical energy.
Question 39. [Sound]
John is trying to create musical notes using water-filled bottles, as shown in the picture.

Which of the bottles is likely to produce a musical note with the highest pitch? Give
reasons.
Answer: Bottle -B is likely to produce a musical note with the highest pitch. Frequency is inversely proportional to the length of the air column. As the length of air column in bottle- B is minimum, hence the frequency will be maximum as compared with other bottles.
Question 40. [Sound]
When Shyam, the band leader, struck both the bass drum and the kettle drum with equal force, the bass drum emitted a sound measuring 120dB, whereas the kettle drum produced a sound of 90dB. Explain this discrepancy in the loudness.
Answer: Surface area of bass drums is bigger than that of kettle drums. We know, larger the surface area louder is the sound produced.
Question 41. [Electricity and Magnetism]
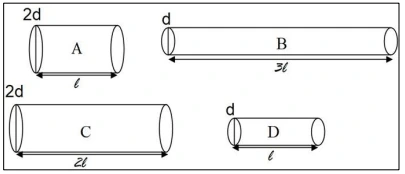
In the above diagram, calculate the ratio of the resistances A, B, C and D.
Answer:
Let the resistance of D be 𝑥 . Resistance is directly proportional to length and inversely proportional to cross-sectional area. Therefore, the resistances of A, B and C will be 𝑥/4, 3𝑥 and 2𝑥/4 respectively.
Therefore, the ratio of their resistances will be
𝑥/4 : 3𝑥 : 2𝑥/4
=𝑥/4 : 3𝑥 : 𝑥/2
=𝑥/4 x4 : 3𝑥 x4 : 𝑥/2 x4
= x : 12x :2x
= 1 : 12 : 2
Question 42. [Electricity and Magnetism]
There are two copper wires of length ratio 1 : 2 that have their cross-sectional areas in the ratio 1 : 4. What will be the ratio of their:
(a) resistances?
(b) specific resistances?
Answer:
(a) 𝑅1 : 𝑅2 = የ×1/1 : የ×2/4
∴ 𝑅1 : 𝑅2 = 1 : 1/2= 2 : 1
(b) As the material is same, therefore the resistivity of the two wires will be same. Hence, ratio = 1 : 1
Question 43. [Light]
AB is an object and PQ is its real, inverted image. The lengths of AB and PQ are equal. This is possible when a lens is present between the object and its image.
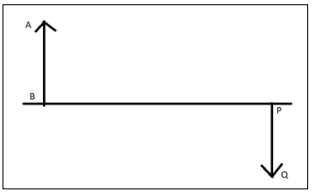
(a) What kind of lens is used here? Also, state the position of the lens and where it is to be placed.
(b) Name a device where this lens action is used.
Answer: (a) Convex lens. Lens is placed at the midpoint of the distance between the object and the image.
(b) Photocopier / xerox machine / intermediate lens in a terrestrial telescope.
Question 44. [Heat]
The two metals A and B have their specific heat capacities in the ratio 2 : 3. If they are supplied the same amount of heat, then
(a) which metal piece will show a greater rise in temperature if their masses are the same?
(b) calculate the ratio in which their temperatures rise, if the mass ratio of metal A and metal B is 3 : 5.
Answer: (a) Metal A. Specific heat capacity of A is less. So, it will require less heat to rise its temperature.
(b) As heat energy supplied (H) is same. Therefore, (m c T)A = (m c T)B
or, 3a x 2b x TA = 5a x 3b x TB
or, 2TA = 5TB
or, TA : TB = 5 : 2
Question 45. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
Soumya took two right circular cones of the same vertical height. One of the two cones is a solid one, while the other is hollow from inside. By measuring the cross-sectional areas of the cones and from the knowledge of symmetry, by using suitable formulas, he found the positions of the centre of gravity of both cones. He found that the difference is about 1.5 cm. What is the vertical height of the two cones?
Answer:
C.G. of hollow cone is h/3 from base and that of solid cone is h/4 from base.
Therefore, ℎ/3 − ℎ/4 = 1.5
∴ 4h – 3h/12 = 1.5
or, ℎ/12 = 1.5
∴ ℎ = 1.5 × 12 = 18 𝑐𝑚
Question 46. [Sound]
Seismic waves have different frequencies. During earthquakes, why are short-length buildings more prone to damage caused by high-frequency seismic waves?
Answer: Natural frequency of a body is inversely proportional to the length of the body. High frequency seismic waves can resonate with short length buildings. Amplitude is increased during resonance. Due to the large amplitude of vibration, it can cause more damage to the buildings.
Question 47. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
Will the centre of gravity of a hollow sphere filled half with mercury and half with oil be identical to that of an empty hollow sphere? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer: No.
The Centre of gravity will shift towards the mercury side as the position of the centre of gravity depends on the distribution of mass.
Question 48. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
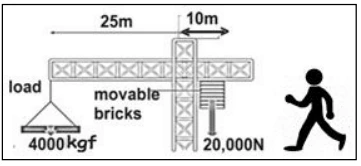
(a) In the diagram, is the worker attempting to raise or lower the load?
(b) Justify your answer to (a) with the necessary calculation.
Answer: (a) Lower
(b) 4000 x 10 x 25 > 20000 x 10
10,00,000 Nm > 2,00,000 Nm
Question 49. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
The graph shows load against effort for a lever with load and effort on the same side of the fulcrum.
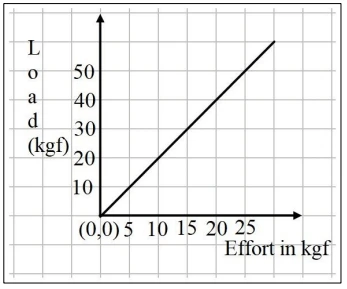
(a) Which feature of the load and effort graph must be calculated to determine mechanical advantage?
(b) Which class does this lever belong to?
Answer: (a) slope
(b) Class II lever
Question 50. [Heat]
(a) Convert to SI unit: 1J/g 0F
(b) Why does 1g of water at 00C have 336J more heat energy than 1g of ice at 00C?
Answer: (a) 1 x 1.8 x 1000 J/kg0C = 1800 J/kg0C
(b) 336J of energy is used to increase the potential energy due to an increase in intermolecular separation, so the latent heat of ice is 336 J.
Question 51. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
Match the columns by choosing the body part and corresponding mechanical lever of the same class.
| Human body part | Mechanical lever |
| i. Nodding head | (a) Bottle Opener |
| ii. Lifting body weight on your toes. | (b) Tongs |
| (c) See-Saw |
Answer: i – (c)
ii – (a)
Question 52. [Electricity and Magnetism]
Redraw the diagram by linking points A, B, and C to points X, Y, and Z on the socket.
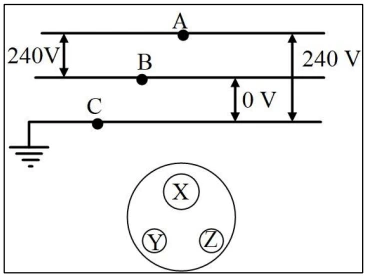
Answer:
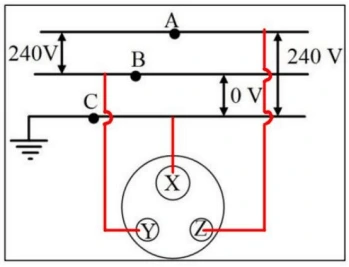
In the socket, opening X connects to earth wire, the opening Z connects to live wire and Y connects to neutral wire.
Question 53. [Sound]
Ashish, Sameer, Aditya and Mohit were sitting on the terrace of Ashish’s house listening to the songs playing on Aditya’s mobile phone. Mohit, sitting in one corner, a little distance away from the others, requests to increase the volume of the songs. But Aditya says the volume is full. Sameer, being a smart guy, gets up, goes into the kitchen, brings an empty steel glass, places the mobile phone inside it and solves the problem. What is the reason for Sameer to keep the mobile phone in the glass?
Answer: Loudness increases with the increase in the surface area of vibration. By placing the mobile phone in the glass, the surface area of vibration increases, transferring more energy in the medium and increasing the loudness.
Question 54. [Electricity and Magnetism]
You are given three resistors of magnitude 3 Ω each. You can join them either in a series or in a parallel combination. How will you arrange them so that the equivalent resistance would become:
(a) maximum
(b) minimum
(Your answer must be accompanied by proper mathematical calculations)
Answer: (a) Equivalent resistance would become maximum when they are combined in series.
R (max) = 3 + 3 + 3 = 9 Ω
(b) Equivalent resistance would become minimum when they are combined in parallel.
I/R = ⅓ + ⅓ + ⅓ = 1
R (min) = 1 Ω
Question 55. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
In a gold atom (atomic number 79), an electron revolves around the nucleus in a circular orbit. There is a strong electrostatic force between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electron. Though the total positive charge possessed by the nucleus is much higher than the negative charge of the electron, there is no displacement of the electron in the direction of the force.
(a) Name the force responsible for the movement of the electron around the nucleus in its own orbit.
(b) In the absence of such force, what would happen to the movement of the electron?
Answer: (a) Centripetal force which is electrostatic force.
(b) In the absence of such force, the electron would have moved in straight line along the tangent to the circular path.
Question 56. [Electricity and Magnetism]
A straight wire is passed vertically through cardboard sprinkled with iron filings.
(a) When current is passed through the wire in the upward direction, it is seen that the iron fillings are arranging themselves in a definite pattern. Why?
(b) What would happen to this arrangement if more current were passed through the wire?
Answer: (a) When the current is passed through the wire, a magnetic field is generated around the wire.
(b) The concentration of magnetic field lines will increase/the number of concentric circles will increase up to a greater distance.
Question 57. [Heat]
On a hot summer day, we often put ice cubes to cool the water. Why?
Answer: We put ice cubes into the water because every 1 g of ice at 00C extracts 336 J of heat from hot water as its latent heat of fusion. Hence, the temperature of the water falls sharply.
Question 58. [Electricity and Magnetism]
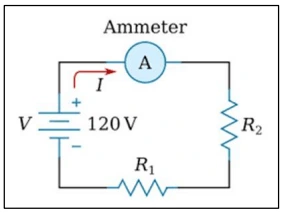
In the given circuit diagram, Minakshi replaced the ammeter by a voltmeter by mistake. Will this circuit work?
Answer: Voltmeter is a high-resistance device. Ideally, its resistance is infinite. So, if by mistake, the ammeter is replaced by the voltmeter, the total resistance of the circuit will also become infinite.
In that case, the current flowing through the circuit will almost become zero, and the circuit will not work properly.
Question 59. [Force, Work, Power and Energy]
A metre rod is half made of copper and half made of iron. If the mass of the copper part is 900 g and the mass of iron is 800 g, then calculate the position at which the rod can remain in equilibrium.
Answer:
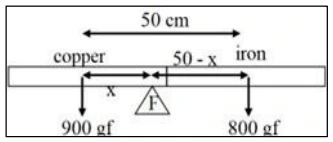
The distance between their C.G. is 50 cm
900 × 𝑥 = 800(50 − 𝑥)
ஃ900𝑥 = 40000 − 800𝑥
ஃ1700𝑥 = 40000
ஃ 𝑥 = 40000/17 = 23.53 cm
It will be balanced at a distance 23.53 cm from the end of copper.
Question 60. [Electricity and Magnetism]
The diagram below shows a copper conductor placed along the east-west direction.
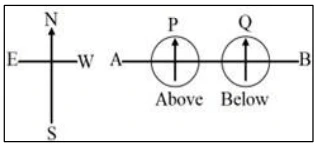
Magnetic compass P is present above the conductor, and Q is below the conductor. If current is passed through the wire from A to B, then which of the two compasses will show prominent deflection and why?
Answer: Compass P.
This is because the direction of magnetic field produced around the conductor for compass Q is in the same direction but it is opposite to the compass P so in order to align in the direction, P will show deflection.
Question 61. [Heat]
The difference between the temperature of water at the bottom and the top of a waterfall is 0.20C. Calculate the height of the waterfall. [g = 10 N kg-1, Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 0C-1]
Answer: By principle of conservation of energy
𝑚𝑔ℎ = 𝑚𝑐𝛥𝑡
10 × ℎ = 4200 × 0.2
ℎ =840/10
= 84 𝑚
Question 62. [Light]
The diagram shows straw partially immersed in water in the glasses.

(a) Why does the straw in water appear thicker as compared to the straw outside water?
(b) Why does the straw appear discontinuous in water?
Answer: (a) The surface of the glass with water is curved so it acts like a convex lens. Thus, due to the refraction through a convex lens it appears bigger (thicker).
(b) Due to refraction, when light passes through water, lateral displacement takes place which shifts the position of the image and makes it appear discontinuous.
Question 63. [Light]
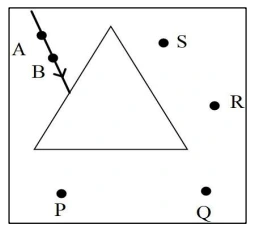
The above diagram shows a triangular prism used for tracing the path of ray AB due to the refraction through the prism. Observe the diagram and answer the following:
(a) State the correct eye position from the points P, Q, R and S to see the images of the points A and B in the same line through the prism.
(b) If the ray, after entering the prism, suffers total internal reflection, then which would be the appropriate position out of P, Q, R, and S to see the image due to TIR?
Answer: (a) Point Q
(b) S, R
ICSE 10 Physics Competency Based Questions Solution:
ICSE Related Links
Competency Focused Practice Questions
Chapter-wise Quiz/MCQ/Test:
ICSE Chapter wise Quiz For Class 6
ICSE Chapter wise Quiz For Class 7
ICSE Chapter wise Quiz For Class 8
ICSE Chapter wise Quiz For Class 9
ICSE Chapter wise Quiz For Class 10
Sample Papers
Board Papers
ICSE Class 9 Board Exam Papers
ICSE Class 10 Board Exam Papers
CBSE Related Links
Chapter wise Quiz/MCQ/Test
CBSE Chapter-wise Quiz for Class 6
CBSE Chapter-wise Quiz for Class 7
CBSE Chapter-wise Quiz for Class 8
CBSE Chapter-wise Quiz for Class 9
CBSE Chapter-wise Quiz for Class 10
Sample Papers
Board Papers
CBSE Class 10 Previous years’ Board Papers
Subscribe to our YouTube channel for more educational updates.

